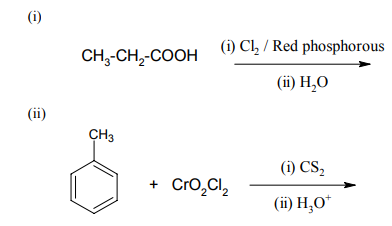
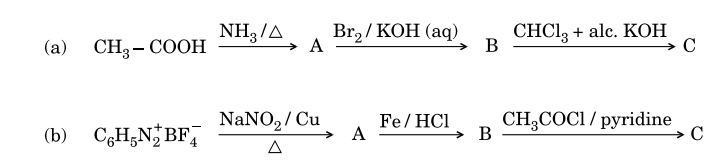1.State briefly the principles involved in the following operations in metallurgy. Give an example.
(i) Hydraulic washing.
(ii) Zone refining.
2. i) What type of deviation from Raoult’s law is observed, when two volatile liquids A and B on mixing produce a warm solution? Explain with the help of a well labeled vapour pressure graph.
ii) Consider separate solutions of 0.5 M CH3OH, 0.250 M KCl (aq) and 0.125 M Na3PO4 (aq). Arrange the above solutions in the increasing order of their Van’t Hoff factor.
3.Write the Nernst equationand calculate the emffor the following cell at 298 K: Mg(s) / Mg2+ (0.001 M) // Cu2+ (0.0001 M) / Cu(s)
How does Ecell vary with the concentration of both Mg2+ and Cu2+ ions? (Given Eocell= 2.71 V)
4.An organic compound ( A ) has characteristic odour. On treatment with NaOH, it forms compounds ( B ) and ( C ). Compound ( B ) has molecular formula C7H 8Owhich on oxidation gives back ( A ). The compound ( C ) is a sodium salt of an acid. When ( C ) is treated with soda-lime, it yields an aromatic compound ( D ). Deduce the structures of ( A ), ( B ), ( C ) and ( D ). Write the sequence of reactions involved.
................................ Advertisement ................................
5.(a) Give one chemical test to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds:
(i) Methylamine and dimethylamine.
(ii) Aniline and benzylamine
(b) Write the structures of different isomers corresponding to the molecular formula C3H9N, which will liberate nitrogen gas on treatment with nitrous acid.
6.(a) Exemplify the following reactions:
(i) Rosenmund reduction reaction.
(ii) Kolbe electrolysis reaction.
(b) Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their reactivity towards HCN:
Acetaldehyde, Acetone, Di-tert-butyl ketone.
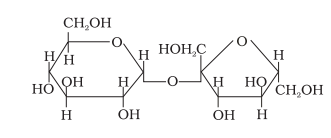
7.(i) Which of the following biomolecule is insoluble in water? Justify.
Insulin, Haemoglobin, Keratin.
(ii) Draw the Haworth structure for α-D-Glucopyranose.
(iii) Write chemical reaction to show that glucose contains aldehyde as carbonyl group.
8.(i) Identify the monomer in the following polymeric structure:

(ii) On the basis of forces between their molecules in a polymer to which class does neoprene belong?
(iii) Can both addition and condensation polymerization result in the formation of a copolymer?
................................ Advertisement ................................
9.(a) Predict the products of the following reactions:
(b) Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of acid strength:
Benzoic acid, 4-Nitrobenzoic acid, 4-Methoxybenzoic acid.
10.When 1 mol of NaCl is added to 1 litre of water, the boiling point of water increases. On the other hand, addition of 1 mol of methyl alcohol to one litre of water decreases the boiling point of water. Explain why does this happen.
11.Value of standard electrode potential for the oxidation of Cl– ion is more positive than that of water, even then in the electrolysis of aqueous sodium chloride solution, why is Cl– oxidised at anode instead of water?
12.How copper is extracted from low grade copper ores?
13.Calculate the volume of 0.1 M NaOH solution required to neutralise the products formed by dissolving 1.1 g of P4O6 in H2O.
................................ Advertisement ................................
14.A complex of the type [M (AA)2X2]n+ is known to be optically active. What does this indicate about the structure of the complex? Give one example of such complex.
15.Predict the major product formed on adding HCl to iso butylene and write the IUPAC name of the product. Explain the mechanism of the reaction.
16.Explain why rate of reaction of Lucas reagent with three classes of alcohols different? Give chemical equations wherever required.
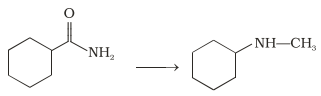
17.A primary amine, R—NH2 can be reacted with alkyl halide, RX, to get secondary amine, R2NH, but the only disadvantage is that 3° amine and quaternary ammonium salts are also obtained as side products. Can you suggest a method where CH3NH2 forms only 2° amine?
18.Label the glucose and fructose units in the following disaccharide and identify anomeric carbon atoms in these units. Is the sugar reducing in nature?Explain.
................................ Advertisement ................................
19.Components of a binary mixture of two liquids A and B were being separated by distillation. After some time separation of components stopped and
composition of vapour phase became same as that of liquid phase. Both the components started coming in the distillate. Explain why this happened.
20.Identify the cathode and anode in the cell written below.
Cu | Cu2+ || Cl– | Cl2 , Pt
Write the reduction half reaction and oxidation half reaction of the cell.
21.With the help of an example explain how one can separate two sulphide ores by Froth Floatation method.
22.White phosphorus reacts with chlorine and the product gets hydrolysed in the presence of water to produce HCl. Calculate the mass of HCl obtained by
the hydrolysis of the product formed by the reactions of 62 g of white phosphorus with chlorine in the presence of water.
................................ Advertisement ................................
23.A coordination compound CrCl3.4H2O precipitates AgCl when treated with AgNO3. The molar conductance of the solution of coordination compound corresponds to a total of two ions. Write structural formula of the compound and name it.
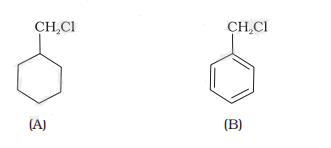
24.Which of the following compounds would undergo S
N1 reaction faster and why?
25.Ethers can be prepared by Williamson synthesis in which an alkyl halide is reacted with sodium alkoxide. Explain why di-tert-butyl ether can’t be
prepared by this method.
26.Suggest a route by which the following conversion can be accomplished.
................................ Advertisement ................................
27.Draw a neat labelled diagram of a method used to concentrate Zinc blende. State the principle involved in chromatography. Write the name and the formula of any one ore of iron.
28.(a) Draw a neat labelled diagram of a semiconductor formed when silicon is doped with an element of group 13.
(b) Name and define the type of defect found in NaCl crystal. What is an octahedral void?
29.(a) Based on the nature of intermolecular forces, classify the following solids :
Silicon carbide, Argon
(b) ZnO turns yellow on heating. Why ?
(c) What is meant by groups 12-16 compounds ? Give an example.
30.(a) The cell in which the following reaction occurs :
2 Fe3+ (aq) + 2 I-(aq) --> 2 Fe2+ (aq) + I2(s)
has Eocell = 0·236 V at 298 K. Calculate the standard Gibbs energy of the cell reaction. (Given : 1 F = 96,500 C mol -1>)
(b) How many electrons flow through a metallic wire if a current of 0·5 A is passed for 2 hours ? (Given : 1 F = 96,500 C mol -1)
31.(a) What type of isomerism is shown by the complex [Co(NH3)5(SCN)]2+?
(b) Why is [NiCl4]2- paramagnetic while [Ni(CN)4]2- is diamagnetic ? (Atomic number of Ni = 28)
(c) Why are low spin tetrahedral complexes rarely observed ?
32.Write one difference in each of the following :
(a) Multimolecular colloid and Associated colloid
(b) Coagulation and Peptization
(c) Homogeneous catalysis and Heterogeneous catalysis
................................ Advertisement ................................
33.(a) Write the dispersed phase and dispersion medium of milk.
(b) Write one similarity between physisorption and chemisorption.
(c) Write the chemical method by which Fe(OH)3 sol is prepared from FeCl3.
34.A first order reaction takes 20 minutes for 25% decomposition. Calculate the time when 75% of the reaction will be completed.
(Given : log 2 = 0·3010, log 3 = 0·4771, log 4 = 0·6021)
35.The following compounds are given to you :
2-Bromopentane, 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane, 1-Bromopentane
(a) Write the compound which is most reactive towards SN2 reaction.
(b) Write the compound which is optically active.
(c) Write the compound which is most reactive towards β-elimination reaction.
................................ Advertisement ................................
36.Write the principle of the following :
(a) Zone refining
(b) Froth floatation process
(c) Chromatography
37.Write the structures of compounds A, B and C in the following reactions :
38.Write the structures of the monomers used for getting the following polymers :
(a) Nylon-6,6
(b) Melamine-formaldehyde polymer
(c) Buna-S
39.Define the following :
(a) Anionic detergents
(b) Limited spectrum antibiotics
(c) Antiseptics
40.Give reasons for the following :
(a) Acetylation of aniline reduces its activation effect.
(b) CH3NH2 is more basic than C6H5NH2.
(c) Although -NH2 is o/p directing group, yet aniline on nitration gives a significant amount of m-nitroaniline.
................................ Advertisement ................................
41.An element crystallizes in a b.c.c lattice with cell edge of 400pm.Calculate the density if 250g of this element contain 2.5 x 1024 atoms?
42.Calculate the freezing point of a solution when 3g of CaCl2(M = 111g mol-1) was dissolved in 100g of water, assuming CaCl2 undergoes complete ionization. (Kf for water = 1.86K kg mol-1)
43.Account for the following:
(i)Fe(OH)3 sol is positively charged
(ii) The extent of physical adsorption decreases with rise in temperature
(iii) A delta is formed at appoint where river enters the sea.
44.Explain mechanism of free radical polymerization.
45.Write IUPAC names of the following:
(i) K3[Fe(C2O4)3]
(ii) [PtCl(NH3)5]Cl3.
(iii) [PtCl(NH2CH3)(NH3)2]Cl.
46.Account for the given statement.
(i) During the preparation of ammonia derivatives from aldehydes or ketones, pH is controlled.
(ii) Formaldehyde gives cannizzaro’s reaction but acetaldehyde does not.
(iii) Carboxylic acids do not give characteristics reactions of carbonyl compounds
................................ Advertisement ................................
47.An element X with atomic mass 60g/mole has a density 6.23g/cm3 . If the edge length of unit cell is 400pm, identify the type of cubic unit cell. Calculate the radius of an atom of this element. (Avagadro number= 6x1023 mole-1)
48.Activation energy of a reaction at 300K is 55KJ/mole. When the same reaction is carried out in the presence of a catalyst activation energy is lowered to 45 KJ/mole at 300K. Determine the extent to which the rate of the reaction is increased.