Solutions : Important Questions And Answers
List of Questions and Answers
1.Define Electromotive force of the cell (emf).
Ans:
The potential difference between the two electrodes of a galvanic cell is called the cell
potential and is measured in volts. The cell potential is the difference between the electrode
potentials (reduction potentials)of the cathode and anode. It is called the cell electromotive
force (emf) of the cell when no current is drawn through the cell.
2.Copper does not dissolve in HCL but dissolves in Nitric Acid. Why?
Ans:
Hydrogen ions cannot oxidise Cu due to which, Cu does not dissolve in HCl.Whereas in nitric
acid it is oxidised by nitrate ion and not by hydrogen ion.
................................ Advertisement ................................
3.Explain Working of Daniell Cell.
Ans:
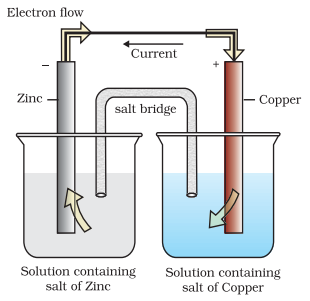
Daniell cell having electrodes of zinc and copper dipping in the solutions of their respective
salts.
In the Daniell cell, copper and zinc electrodes are immersed in a solution of copper(II)
sulfate and zinc sulfate respectively. The reaction is as follows:
![]()
This reaction is a combination of two half reactions whose addition gives the overall cell
reaction:
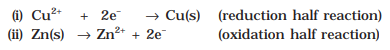
These reactions occur in two different portions of the Daniell cell.The reduction half reaction occurs on the copper electrode while the oxidation half reaction occurs on the zinc electrode. These two portions of the cell are also called half-cells or redox couples. The copper electrode may be called the reduction half cell and the zinc electrode,the oxidation half-cell.
4.What is a Electrochemical cell?
Ans:
Electrochemical cell is a device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy based
on the result of spontaneous redox reaction.
5.What are the uses of Electrochemical cell?
Ans:
Electrochemical cells are extensively used for
determining the pH of solutions
solubility product
equilibrium constant
other thermodynamic properties
for potentiometric titrations.
6.Can you store copper sulphate solutions in a zinc pot?
Ans:
No, we cannot store copper sulphate in zinc pot.The reason behind it is copper is less reactive
to zinc, so zinc will react with copper sulphate and copper ions will get displaced from
solution as metallic copper.
Here is the reaction for :
Zn + CuSo
4 ----> ZnSo
4 + Cu
................................ Advertisement ................................
7.How would you determine the standard electrode potential of the system Mg 2+|Mg?
Ans:
The standard electrode potential is given as :
![]()
With respect to above we can get the standard electrode potential of Mg2+| Mg.
We have a cell with cathode as Mg|MgSO4(aq 1M) and anode as standard hydrogen electrode.
Cathode : Mg|Mg2+ (Mg dipped in 1M MgSO4 solution)
Emf of the Cell : Pt(s),H2(g,1bar) || Mg2+(aq 1M) | Mg(s)
The emf of the cell is measured and this measured emf is the standard electrode potential
of Mg2+| Mg
Using Formula:
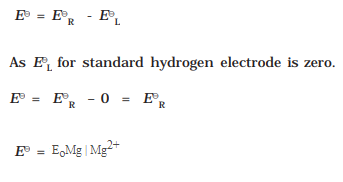
8.Represent the cell in which the following reaction takes place
Mg(s) + 2Ag
+(0.0001M) --> Mg
2+(0.130M) + 2Ag(s)
Calculate its E
(cell) if E
o
(cell) = 3.17 V.
Ans:
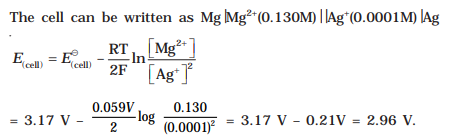
9.Calculate the equilibrium constant of the reaction:
Ans:
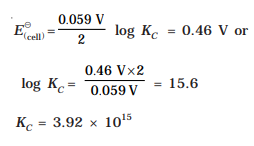
10.The standard electrode potential for Daniell cell is 1.1V.
Calculate the standard Gibbs energy for the reaction:
![]()
Ans:
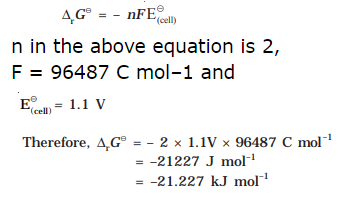
11.State Kohlrausch’s Law.
Ans:
The law states that limiting molar conductivity of an electrolyte can be represented as
the sum of the individual contributions of the anion and cation of the electrolyte.
................................ Advertisement ................................
12.State Faraday’s Law of Electrolysis.
Ans:
First Law:The amount of chemical reaction which occurs at any electrode during electrolysis
by a current is proportional to the quantity of electricity passed through the electrolyte
(solution or melt).
Second Law:The amounts of different substances liberated by the same quantity of electricity
passing through the electrolytic solution are proportional to their chemical equivalent weights
(Atomic Mass of Metal ÷ Number of electrons required to reduce the cation).
13.Calculate the emf of the cell in which the following reaction takes place
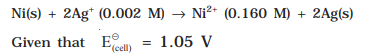
Ans:

14.The cell in which the following reaction occurs:
Calculate the standard Gibbs energy and the equilibrium constant of the cell reaction.
Ans :

15.Calculate emf of the following cell
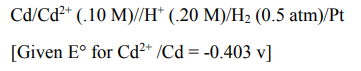
Ans:

16.Define Fuel Cells.
Ans:
Fuel cells are cells designed to convert the energy of combustion of fuels like hydrogen,
methane, methanol, etc. directly into electrical energy.
................................ Advertisement ................................
17.Why does the conductivity of a solution decrease with dilution?
Ans:
Conductivity of solution is directly proportional to the number of ions present in a unit
volume of solution.The ions present in the solution are responsible for carrying current.With
dilution the ions are decreased , thus causing decrease in conductivity of solution.
18.Calculate emf of the following cell at 298K
Zn | Zn
2+ (10
-4 M) || Cu
2+ (10
-2M) | Cu
Given E
0
Zn2+/Zn=-0.76V , E
0
Cu2+/Cu=+0.34V
Ans:

19.State Faraday’s Laws of Electrolysis.
Ans:
As per First Law it says:
The amount of chemical reaction which occurs at any electrode during electrolysis by a current
is proportional to the quantity of electricity passed through the electrolyte (solution or
melt).
As per Second Law it says: The amounts of different substances liberated by the same quantity
of electricity passing through the electrolytic solution are proportional to their chemical
equivalent weights (Atomic Mass of Metal ÷ Number of electrons required to reduce the cation).
20.What is the effect of temperature on molar conductivity?
Ans:
Molar conductivity of an electrolyte increases with increase in temperature.
21.A solution of CuSO 4 is electrolysed for 10 minutes with a current of 1.5 amperes. What is the mass of copper deposited at the cathode?
Ans:

22.Suggest a list of metals that are extracted electrolytically.
Ans:
Metals which are highly reactive such as sodium, potassium, calcium, lithium, magnesium,
aluminium are extracted electrolytically.
................................ Advertisement ................................
23.If a current of 0.5 ampere flows through a metallic wire for 2 hours, then how many electrons would flow through the wire?
Ans:
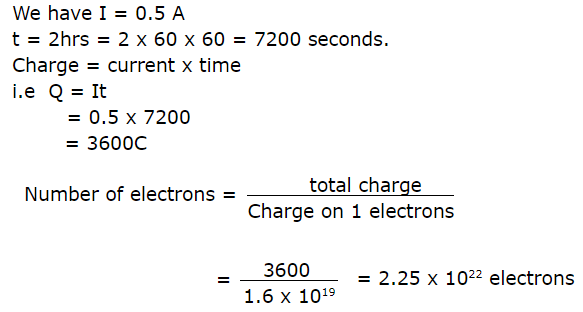
24.What is Fuel Cell?
Ans:
A fuel cell is a galvanic cell for converting the energy of a fuel directly into electrical
energy without use of a heat engine.
25.What is meant by Faraday‘s constant?
Ans :
Faraday‘s constant is the quantity of electricity carried by one mole of electrons. 1 F
= 96500 C/mol
................................ Advertisement ................................
26.Give reasons:
(a) Rusting of iron is quicker in saline water than in ordinary water
(b) Aluminium metal cannot be produced by the electrolysis of aqueous solution of aluminium
salt.
Ans :
(a) The conductivity of saline water is more than ordinary water.
(b) Al is highly reactive and cannot be reduced easily as compared to Al
3+ ions, water is reduced easily since E0 reduction for water is higher.
27.Enlist the factors affecting corrosion?
Ans:
Factors affecting corrosion are –
a) Water and air
b) Presence of electrolytes in water.
c) Presence of gases like CO
2 , SO
2.
28.Define Molar Conductivity.
Ans:
It the conductance due to all the ion produced from 1 mole of an electrolyte in Vcm3 of
the solution. It is represented by λcm at conc. ‘C’ and λ∞m at infinite dilution.
................................ Advertisement ................................
29.State difference between a primary battery and secondary battery
Ans:
| Primary Battery | Secondary Battery |
| In primary batteries ,the reaction occurs only once and after use over a period of time battery becomes dead and cannot be reused again | A secondary battery after use can be recharged by passing current through it in the opposite direction so that it can be used again. |
| used commonly in our transistors and clocks | commonly used in automobiles and inverters |
| Dry cell, mercury cell are primary batteries | Lead Storage battery are secondary batteries. |
30.Galvanized iron does not corrode even if the coating of zinc is broken. Explain why?
Ans :
Zinc is more reactive than iron, and happens to loose electrons and acts as a anode and
does not allow iron to lose electron and here iron acts as a cathode.So as long as coating
of zinc is present on the surface of iron it will prevent it from corroding and behave as
a sacrificial electrode and lose electrons.
31.Write the name of a chemical substance which is used to prevent corrosion.
Ans :
bisphenol
................................ Advertisement ................................
32.Give reasons for :
(a) For a weak electrolyte, its molar conductivity of dilute solution increases sharply
as the concentration of solution is decreased.
(b) Molar conductivity of a strong electrolyte like KCl decrease slightly while increasing
concentration?
Ans :
(a) In case of weak electrolyte ,when the concentration of solution is decreased the degree
of ionisation increases i.e there is a increase of ions in the solutions thus increases the
molar conductivity.
(b) The molar conductivity of a strong electrolyte decreases slightly with the increase
in concentration. This decrease is due to the increase in interionic attractions as a result
of greater number of ions per unit volume. With dilution, the ions are far apart, inter ionic
attractions become weaker and conductance increases.