Important 5 Marks Questions From Board Papers
List of 5 Marks Questions
1.(a) Why osmotic pressure is a better criteria for measuring the molecular mass of macromolecules as compared to elevation of boiling point or depression of freezing point?
(b) At 300K, 36g of glucose present in one litre of its solution has an osmotic pressure of 4.98 bar. If the osmotic pressure of the solution is 1.52 bar at the same temperature,what would be its concentration?
(b) At 300K, 36g of glucose present in one litre of its solution has an osmotic pressure of 4.98 bar. If the osmotic pressure of the solution is 1.52 bar at the same temperature,what would be its concentration?
2.(a) An aqueous solution containing 4% nonvolatile solute exerts a pressure of 1.002 bar at the normal boiling point of the solvent. What is the molar mass of the solute?
(b)Why is common salt used to clear the snow off the road?
(c)Why does water stop boiling when sugar is added to it when it is boiling?
(b)Why is common salt used to clear the snow off the road?
(c)Why does water stop boiling when sugar is added to it when it is boiling?
3.Ozonolysis of compound ‘A’ (C7H14) yields a mixture containing compounds ‘B’ and ‘C’. Both ‘B’ and ‘C’ give positive 2.4 - DNP test and Tollen’s test. ‘B’ undergoes Cannizzaro’s reaction. ‘C’ undergoes aldol condensation to give ‘D’. ‘B’ is also obtained by the reaction of 2, 2 –dimethylpropanol with PCC. Deduce the structures of A, B, C and D and justify your answer by giving the equations of the reactions involved.
4.An aromatic compound "A" (C8H6) reacts with dil. H2SO4 and HgSO4 giving "B", which upon reaction with NaOH and I2 gives compounds "C" and "D". "D" upon reaction with soda lime gives a hydrocarbon "E", which on reaction with CH3COCl in the presence of anhydrous aluminium chloride gives "B". Identify "A", "B", "C", "D" and "E" and write the equations of the reactions involved.
5.Discuss the method of extraction of iron from its ore with the help of equations and diagram.Also discuss the thermodynamic principle of the reduction of its oxide into metal.
................................ Advertisement ................................
6.The choice of reducing agent in a particular case depends on thermodynamic principles.
How far do you agree with this statement? Explain the feasibility of the following reduction
reactions on the bases of thermodynamic principles.
i) reduction of Al2O3 with CO
ii) Reduction of Fe2O3 with CO
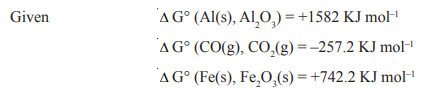
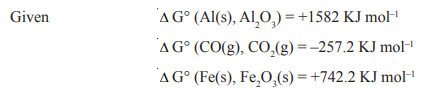
7.Explain with equations:-
a) Cannizaro’s Reaction
b) Mole’s Fraction
a) Cannizaro’s Reaction
b) Mole’s Fraction
8.How will you explain for the following occurrence?
a) +3 oxidation state becomes more and more stable from As to Bi in the group.
b) Sulphur in vapour state exhibits para-magnetism.
a) +3 oxidation state becomes more and more stable from As to Bi in the group.
b) Sulphur in vapour state exhibits para-magnetism.
9.Define octet rule. Write its significance and limitations.
10.Addition of HBr to propene yields 2-bromopropane , while in the presence of benzoyl peroxide, the same reaction yields 1-bromopropane. Explain and give mechanisim?
11.What is the difference between molecular and empirical formula?A compound contain 4.07% hydrogen , 24.27% oxygen and 71.65% chlorine. Its molecular mass is 98.26 g . What are its empirical and molecular formulas?
................................ Advertisement ................................
12.State photo electric effect. The work function for caesium atom is 1.9 eV.
13. At 473K, equlibirium constant Kc for decomposition of phosphorus pentachloride,PCl5 is 8.3 x 10-3.If decomposition is depicted as,
PCl5(g) PCl3 (g) + Cl2(g) ∆rH°= 124.0 kJ mol-1
a) Write an expression Kc for the reaction.
b) What is the value of Kc for the reverse reaction at the same temperature?
c) What would be the effect on Kc if (i) more PCl5 is added (ii) pressure is increase ?
a) Write an expression Kc for the reaction.
b) What is the value of Kc for the reverse reaction at the same temperature?
c) What would be the effect on Kc if (i) more PCl5 is added (ii) pressure is increase ?
14.Explain the Preparation and properties of K2CR2O7.
15.Explain:-
1. Mole’s Fraction
2. Van’t off factor
1. Mole’s Fraction
2. Van’t off factor
16.Give reasons for the following:-
1. NH3 adsorbed to great extent as compare to N2 gas.
2. ICl is more reactive than I2.
3. +3 oxidation states become more and more stable from As to Bi in the group.
4. Sulphur in vapour state exhibits paramagnetism.
1. NH3 adsorbed to great extent as compare to N2 gas.
2. ICl is more reactive than I2.
3. +3 oxidation states become more and more stable from As to Bi in the group.
4. Sulphur in vapour state exhibits paramagnetism.
17.What is Grignard reagent ? What are the products formed when Grignard reagent react with.
a)(Formaldehyde) (b) (Acetone)
a)(Formaldehyde) (b) (Acetone)
................................ Advertisement ................................
18.Convert the following
(a)(Acetic acid to acetone)
(b) (Acetylene to acetic acid)
(c) (Benzoic acid to Benzaldehyde)
(a)(Acetic acid to acetone)
(b) (Acetylene to acetic acid)
(c) (Benzoic acid to Benzaldehyde)
19.How is ammonia manufactured industrially?
20.
(a) Why does NH3 from hydrogen bond but PH3 does not?
(b) Why are halogens strong oxidizing agents ?
(b) Why are halogens strong oxidizing agents ?
21.(a) The Specifit conductivity of 0.020 M solution of KCl at 298 K is 0.0248 S cm–1 Calculate its molar conductivity.
(b) Define the term a morphous’ Give a few examples of amorphous solids.
(b) Define the term a morphous’ Give a few examples of amorphous solids.
22.Account for the following:-
(a) PCl5 is known but NCl5 is not known.
(b) Sulphur in the vapour state exhibits paramagnetism.
(c) Fluorine exhibits only -1 oxidation state whereas other halogens exhibit +1, +3, +5 and +7 oxidation state.
(d) Noble gases form compounds with fluorine and oxygen only.
(e) Bleaching of flowers by chlorine is permanent while that by sulphur dioxide is temporary why?
(a) PCl5 is known but NCl5 is not known.
(b) Sulphur in the vapour state exhibits paramagnetism.
(c) Fluorine exhibits only -1 oxidation state whereas other halogens exhibit +1, +3, +5 and +7 oxidation state.
(d) Noble gases form compounds with fluorine and oxygen only.
(e) Bleaching of flowers by chlorine is permanent while that by sulphur dioxide is temporary why?
................................ Advertisement ................................
23.Define kohlrausch's law. How does it help in (a) Calculation of o λ for a weak electrolyte and (b) degree of dissociation of a weak electrolyte ?
24.State and explain Roult's law for volatile and nonvolatile solute. Explain the positive deviation from ideal behaviour
with proper example and graph.
25.What is polymerisation ? Define and explain the term-Addition polymerisation and condensation polymerisation with one example each.
26.(a)What are monosaccharides ? How are they classified ?
(b)Explain why glucose forms an oxime but glucosepentaacetate does not.
(b)Explain why glucose forms an oxime but glucosepentaacetate does not.
27.(a) The vapour pressure of ether (md ut = 74) is 442 mn of Hg at 293o K. If 3g of a sample A
is dissolved in 50g of ether, at this temperature, the vapour pressure falls to 426 mm Hg. Calculate, the
molecular mass of A, assuming that the solution is very dilute.
(b) Why is the vapour pressure of a solution of glucose in water is lower than that of water.
(b) Why is the vapour pressure of a solution of glucose in water is lower than that of water.
28.(a) The Half-life time of a first order reaction is 60 minutes. How long will it take to consume 90% of the
reaction.
(b)Express the rate of reaction of the following reaction : 2 N2O5 → 2N2O4+ O2
Using : (i) Concentration change of N2O5
(ii) Concentration change of O2
(b)Express the rate of reaction of the following reaction : 2 N2O5 → 2N2O4+ O2
Using : (i) Concentration change of N2O5
(ii) Concentration change of O2
................................ Advertisement ................................
29.(a) Derive Nerst equation for the cell, Ni(s) |Ni+2 )aq 0.01 M)| |Ag+ (aq 0.1 M)| Ag (s) Also find the cell potential Given :
EoAg+/Ag = 0.80V and Eo Ni2+1/Ni = – 0.25V
(b)Predict the products of electrolysis is each of the following.
(i) an aqueous solution of AgNO3 with Ag electrodes. (ii) An aqueous solution of AgNO3 with platinum.
EoAg+/Ag = 0.80V and Eo Ni2+1/Ni = – 0.25V
(b)Predict the products of electrolysis is each of the following.
(i) an aqueous solution of AgNO3 with Ag electrodes. (ii) An aqueous solution of AgNO3 with platinum.
30.(a)Explain why NH3 is basic while BiH3 is only feebly basic.
(b) Explain why NH3 has highes boiling point the PH3.
(b) Explain why NH3 has highes boiling point the PH3.
31.Discuss the hybridisation Sulphur and structure of the following molecules—
(i) SF6 (ii) SF4 (iii) SCl3
(i) SF6 (ii) SF4 (iii) SCl3
32.(a)Give two Methods of preparation of ethers from alcohol with chemical equations.
(b) Write short not on Williamson synthesis.
(c) Write the structural formula of all possible ethers having the molecular formula C4H10O and name them.
(b) Write short not on Williamson synthesis.
(c) Write the structural formula of all possible ethers having the molecular formula C4H10O and name them.
33.(a)What happens when—
(i)Toulben reacts with Cl2 in presence of FeCl2
(ii) Ethanal is treated with ethanol in the presence of dry HCl gas.
(iii) Benzyl amine reacts with two moles of CH3Cl.
(b) Explain why aldehydes are more reactive than ketones.
(i)Toulben reacts with Cl2 in presence of FeCl2
(ii) Ethanal is treated with ethanol in the presence of dry HCl gas.
(iii) Benzyl amine reacts with two moles of CH3Cl.
(b) Explain why aldehydes are more reactive than ketones.
................................ Advertisement ................................
34.Define entropy. Why is it a state function ? Explain the effect of in areased temperatures on the entropy of a
substance.
35.Why are paramagnetic substances usually coloured ? What is nucleophilic substitution reaction ? Draw the structure of PCl5
36.Define the term ‘molal depression constant’. 4.0g of a substance dissolved in 80.g of water produced a depression of 1.5 k in the freezing point of water. Calculate the molecular mass of the substance. (Given : kfH2O= 1.85 [kg for mol–1]
37.Explain each of the following terms :—
(a)Adsorption (b)Sorption (c)desorption and (d) Shape-Selective catalyst.
(a)Adsorption (b)Sorption (c)desorption and (d) Shape-Selective catalyst.
38.Write giving chemical equations:
(a)Aldol condensation (b)Cannizzaro's reaction (c)Carbyl amine reaction (d)Nitration of benzene
(a)Aldol condensation (b)Cannizzaro's reaction (c)Carbyl amine reaction (d)Nitration of benzene
39.(a)Complete the following reaction:
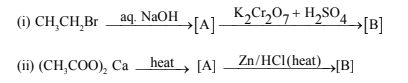 (b) Explain the difference of 1o, 2o and 3o Amines.
(b) Explain the difference of 1o, 2o and 3o Amines.
(c) Find out the molality of 15% solution of H2SO4 by mass.

(c) Find out the molality of 15% solution of H2SO4 by mass.
................................ Advertisement ................................
40.What do you mean by abnormal molecular mass? Explain the factors with suitable examples which bring about the abnormality?
41.What is polymerisation ? Define and explain the term addition polymensation and condensation polymersiaton.Give one example of each.
42.Write IUPAC names of:
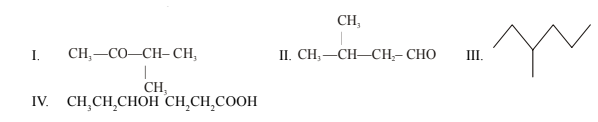
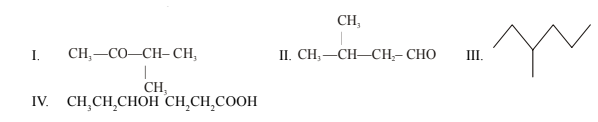
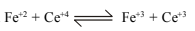
43.Calculate the equilibrium const. for the reaction
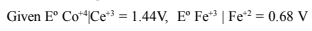
44.Describe the general characteristics of transition elements with special reference to the following.
(a)formation of coloured salt.
(b)Variable oxidation state.
(a)formation of coloured salt.
(b)Variable oxidation state.
45.
Account for the following.
(a) Silver is a transition metal but zinc is not.
(b) the transition metals form a large number of complex compounds.
(c) MnO is basic white Mn2O7 is acidic in nature.
(d) Actinides show more number of oxidation states than lanthanides.
(e) Transition metals have high enthalpies of atomization.
(a) Silver is a transition metal but zinc is not.
(b) the transition metals form a large number of complex compounds.
(c) MnO is basic white Mn2O7 is acidic in nature.
(d) Actinides show more number of oxidation states than lanthanides.
(e) Transition metals have high enthalpies of atomization.
................................ Advertisement ................................
46.
(I) Write chemical equations for the following reactions.
(a) Disproportionation of manganese (VI) in acidic solution.
(b) Acidification of potassium chromate solutions.
(c) Oxidation of nitrite ion by MnO4- in acidic medium.
(II) (i) Which is stronger reducing agent Cr2+ or Fe2+ and why.
(ii) Explain why Cu+ ion is not stable in aqueous solution.
(a) Disproportionation of manganese (VI) in acidic solution.
(b) Acidification of potassium chromate solutions.
(c) Oxidation of nitrite ion by MnO4- in acidic medium.
(II) (i) Which is stronger reducing agent Cr2+ or Fe2+ and why.
(ii) Explain why Cu+ ion is not stable in aqueous solution.
47.
(a) State Henry's law and mention its two applications.
(b) Which of the following has higher boiling point and why.
0.1M NaCl or 0.1 M Glucose
(c) On dissolving 19.5 g of CH2FCOOH in 500 g of water a depression of 10C in freezing point of water is observed. Calculate the Vant Hoff factor. Given Kf = 1.86 K Kg mol-1.
(b) Which of the following has higher boiling point and why.
0.1M NaCl or 0.1 M Glucose
(c) On dissolving 19.5 g of CH2FCOOH in 500 g of water a depression of 10C in freezing point of water is observed. Calculate the Vant Hoff factor. Given Kf = 1.86 K Kg mol-1.
48.(a) State Raoult's law for the solutions containing nonvolatile solute. Give its mathematical expression also.
(b) A solution containing 0.5 g of KCl dissolved in 100 gm of water freezes at -0.240C. Calculate the degree of dissociation of the salt (K for water = 1.860C).
49.
(a) Describe the following reactions.
(i) Canni zaro's reaction.
(ii) Cross aldol condensation.
(b) How will you convert foll:
(i) Methyl cyanide to acetamide
(ii) Acetaldehyde to but 2 enal.
(iii) Ethyl benzene to benzoic acid
(i) Canni zaro's reaction.
(ii) Cross aldol condensation.
(b) How will you convert foll:
(i) Methyl cyanide to acetamide
(ii) Acetaldehyde to but 2 enal.
(iii) Ethyl benzene to benzoic acid
50.
(a) A compound a on oxidation given B (C2H4O2).A reacts with Dil NaOH and on subsequent heating forms C. C on catalytic hydrogenation gives D. Identify A,B, C and D and write down the reaction involved.
(b) Write short notes on
(i) Clemmenson reaction.
(ii) Hell – Volhard – Zelinsky reaction.
(b) Write short notes on
(i) Clemmenson reaction.
(ii) Hell – Volhard – Zelinsky reaction.