The p-Block Elements : Important Questions And Answers
List of Questions and Answers
1.Write the formulae of any two oxoacids of phosphorus.
Ans:
H
3PO
3 and H
3PO
4
2.Explain why fluorine forms only one oxoacid, HOF.
Ans:
It is because of its high electronegativity and small size.
3.Write the formulae of any two oxoacids of chlorine.
Ans:
HClO
3 and HCl0
4.
4.Out of white phosphorus and red phosphorus, which one is more reactive and why?.
Ans:
White phosphorus because it is monomeric and has low bond dissociation enthalpy due to angle
of strain (bond angle 60°).
5.Write the formulae of any two oxoacids of sulphur.
Ans:
H
2SO
4 and H
2SO
3
................................ Advertisement ................................
6.Which allotrope of sulphur is thermally stable at room temperature?
Ans:
Rhombic sulphur.
7.Why are pentahalides more covalent than trihalides?
Ans:
Higher the positive oxidation state of central atom, more will be its polarising power.
Thus pentahalides are more covalent than trihalides.
8.Why is BiH 3 the strongest reducing agent amongst all the hydrides of Groups 15 elements?
Ans:
The reducing character of the hydrides of Group 15 elements increases from NH
3 to BiH
3(Bismuthine) because the reducing character depends upon the stability of the hydride.The
greater the unstability of an hydride,the greater is the its reducing character.Since, BiH
3 is the least stable (because the size of central atom is greatest & therefore its
tendency to form stable covalent bond with small hydrogen atom decreases,as a result the
bond strength decreases) in this series,hence it becomes the strongest reducing agent.
9.Why is N 2 less reactive at room temperature?.
Ans:
Due to the presence of a triple bond between the two nitrogen atoms, the bond dissociation
energy of N
2 (946 kJ mol–1) is very high. Therefore, N
2 is less reactive at room temperature.
10.How does ammonia react with a solution of Cu2+?
Ans:
Cu2+ ions react with excess of ammonia to form a deep blue coloured complex.
Cu
2+ (aq) + 4NH
4OH (aq) --> [Cu(NH
3)
4 ]2+ Tetramminecopper(II) ion(Deep blue) + 4H
2O
11.What is the basicity of H 3PO 4?
Ans:
H
3PO
4
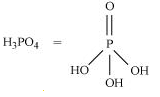
Since there are three OH groups present in H
3PO
4, its basicity is three i.e., it is a tribasic acid.
................................ Advertisement ................................
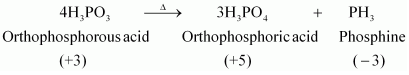
12.What happens when H 3PO 3 is heated?
Ans:
H
3PO
3 ,on heating, undergoes disproportionation reaction to form PH
3 and H
3PO
4. The oxidation numbers of P in H
3PO
3 ,PH
3, and H
3PO
4 are +3, - 3, and +5 respectively. As the oxidation number of the same element is
decreasing and increasing during a particular reaction, the reaction is a disproportionation
reaction.
13.List the important sources of sulphur.
Ans:
Sulphur mainly exists in combined form in the earth's crust primarily as sulphates [gypsum
(CaSO4.2H2O), Epsom salt (MgSO4.7H2O), baryte (BaSO4)] and sulphides [(galena (PbS), zinc
blends (ZnS), copper pyrites (CuFeS2)].
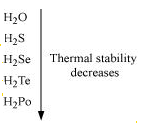
14.Write the order of thermal stability of the hydrides of Group 16 elements.
Ans:
The thermal stability of hydrides decreases on moving down the group. This is due to a decrease
in the bond dissociation enthalpy (H-E) of hydrides on moving down the group.Therefore,
15.Which of the following does not react with oxygen directly?Zn, Ti, Pt, Fe
Ans:
Pt is a noble metal and does not react very easily. All other elements, Zn, Ti, Fe, are
quite reactive. Hence, oxygen does not react with platinum (Pt) directly.
16.Why is H2O a liquid and H2S a gas?
Ans:
H2O has oxygen as the central atom. Oxygen has smaller size and higher electronegativity
as compared to sulphur. Therefore, there is extensive hydrogen bonding in H2O, which is absent
in H2S. Molecules of H2S are held together only by weak van der Waal's forces of attraction.
Hence, H2O exists as a liquid while H2S as a gas.
17.Complete the following reactions:
(i) C2H4 + O2 →
(ii) 4Al + 3O2 →
Ans:
(i) C2H4 + 3O2 → 2CO2 + 2H2O
Ethene + Oxygen Carbon dyoxide + Water
(ii) 4Al + 3O2 → 2Al2O3
Aluminium + Oxygen Alumina
................................ Advertisement ................................
18.What happens when sulphur dioxide is passed through an aqueous solution of Fe(III) salt?
Ans:
SO
2 acts as a reducing agent when passed through an aqueous solution containing Fe(III)
salt. It reduces Fe(III) to Fe(II) i.e., ferric ions to ferrous ions.
2Fe
3+ + SO
2 + 2H
2O → 2Fe
2+ + SO4
2- + 4H
+
19.Why does O3 act as a powerful oxidising agent?.
Ozone is not a very stable compound under normal conditions and decomposes readily on heating to give a molecule of oxygen
and nascent oxygen. Nascent oxygen, being a free radical, is very reactive.
O3
![]() O2 + [O]
O2 + [O]
Ozone = Oxygen + Nascent Oxygen
Therefore, ozone acts as a powerful oxidising agent.
20.How is the presence of SO2 detected?
Ans:
SO
2 is a colourless and pungent smelling gas.
It can be detected with the help of potassium permanganate solution. When SO
2 is passed through an acidified potassium permanganate solution, it decolonizes the
solution as it reduces MnO4- ions to Mn2+ ions
5SO
2 + 2MnO4
- + 2H
2O → 5SO4
2- + 4H
+ + 2Mn
2+
21.Give two examples to show the anomalous behaviour of fluorine.
Following is the list of examples:
(i) It forms only one oxoacid as compared to other halogens that form a number of oxoacids.
(ii) Ionisation enthalpy, electronegativity, and electrode potential of fluorine are much
higher than expected.
22.Why does chlorine water loses its yellow colour on standing?
Ans:
Chlorine water on standing loses its yellow colour due to the formation of HCl and HOCl.
![]()
23.Why is ICl more reactive than I2?
Ans:
ICl is more reactive than I2 because I-Cl bond in ICl is weaker than I-I bond in I
2.
................................ Advertisement ................................
24.Balance the following equation: XeF 6 + H 2O → XeO 2F 2 + HF
Ans:
Balanced equation:
XeF
6 + 2H
2O → XeO
2F
2 + 4HF
25.Sea is the greatest source of some halogens. Comment
Ans:
Sea water contains chlorides, bromides, and iodides of Na, K, Mg, and Ca. However, it primarily
contains NaCl. The deposits of dried up sea beds contain sodium chloride and carnallite,
KCl.MgCl2.6H2O. Marine life also contains iodine in their systems. For example, sea weeds
contain upto 0.5% iodine as sodium iodide. Thus, sea is the greatest source of halogens.
26.Give the reason for bleaching action of Cl2.
Ans:
When chlorine reacts with water, it produces nascent oxygen. This nascent oxygen then combines
with the coloured substances present in the organic matter to oxide them into colourless
substances.
Cl
2 + H
2O → 2HCl + [O]
Coloured substances + [O] → Oxidized colourless substance
27.Why does PCl 5 fume in moisture?
Ans:
PCl5 fumes because it gets hydrolysed to from HCl which fumes in moist air.
![]()
28.Name two poisonous gases which can be prepared from chlorine gas.
Ans:
Two poisonous gases that can be prepared from chlorine gas are
(i) Phosgene (COCl
2)
(ii) Mustard gas (ClCH
2CH
2SCH
2CH
2Cl)
................................ Advertisement ................................
29.Why has it been difficult to study the chemistry of radon?
Ans:
It is difficult to study the chemistry of radon because it is a radioactive substance having
a half-life of only 3.82 days. Also, compounds of radon such as RnF
2 have not been isolated. They have only been identified.
30.Why is helium used in diving apparatus?
Ans:
Air contains a large amount of nitrogen and the solubility of gases in liquids increases
with increase in pressure. When sea divers dive deep into the sea, large amount of nitrogen
dissolves in their blood. When they come back to the surface, solubility of nitrogen decreases
and it separates from the blood and forms small air bubbles. This leads to a dangerous medical
condition called bends. Therefore, air in oxygen cylinders used for diving is diluted with
helium gas. This is done as He is sparingly less soluble in blood.
31.Considering the parameters such as bond dissociation enthalpy, electron gain enthalpy and hydration enthalpy, compare the oxidising power of F2 and Cl2.
Ans:
Fluorine is a much stronger oxidizing agent than chlorine. The oxidizing power depends on
three factors.
1. Bond dissociation energy
2. Electron gain enthalpy
3. Hydration enthalpy
The electron gain enthalpy of chlorine is more negative than that of fluorine. However,
the bond dissociation energy of fluorine is much lesser than that of chlorine. Also, because
of its small size, the hydration energy of fluorine is much higher than that of chlorine.
Therefore, the latter two factors more than compensate for the less negative electron gain
enthalpy of fluorine. Thus, fluorine is a much stronger oxidizing agent than chlorine.
32.Write the conditions to maximize the yield of H 2SO 4 by Contact process.
Ans:
>Manufacture of sulphuric acid by Contact process involves three steps. 1. Burning of ores
to form SO2
2. Conversion of SO2 to SO3 by the reaction of the former with O2 (V2O5 is used in this
process as a catalyst.)
3. Absorption of SO3 in H2SO4 to give oleum (H2S2O7)
The key step in this process is the second step. In this step, two moles of gaseous reactants
combine to give one mole of gaseous product. Also, this reaction is exothermic. Thus, in
accordance with Le Chatelier's principle, to obtain the maximum amount of SO3 gas, temperature
should be low and pressure should be high.
................................ Advertisement ................................
33.Mention three areas in which H2SO4 plays an important role.
Ans:
Sulphuric acid is an important industrial chemicaland is used for a lot of purposes. Some
important uses of sulphuric acid are given below.
(i) It is used in fertilizer industry. It is used to make various fertilizers such as ammonium
sulphate and calcium super phosphate.
(ii) It is used in the manufacture of pigments, paints, and detergents.
(iii) It is used in the manufacture of storage batteries
34.Comment on the nature of two S-O bonds formed in SO2 molecule. Are the two S-O bonds in this molecule equal?
Ans:
The electronic configuration of S is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p4.
During the formation of SO2, one electron from 3p orbital goes to the 3d orbital and S undergoes
sp2 hybridization. Two of these orbitals form sigma bonds with two oxygen atoms and the third
contains a lone pair. p-orbital and d-orbital contain an unpaired electron each. One of these
electrons forms p π- p π bond with one oxygen atom and the other forms p π- d π bond with
the other oxygen. This is the reason SO2 has a bent structure. Also, it is a resonance hybrid
of structures I and II.
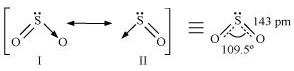 Both S-O bonds are equal in length (143 pm) and have a multiple bond character.
Both S-O bonds are equal in length (143 pm) and have a multiple bond character.
35.Write a balanced equation for the hydrolytic reaction of PCl 5 in heavy water.
Ans:
In moist air ,PCl5 hydrolysis to POCl3 and finally gets converted to phosphoric acid.The
reaction is as follows:
PCL
5 + H
2O → POCl
3 + 2HCl (phosphorus oxychloride)
POCl
3 + H
2O → H
3PO
4 + 3HCl ( phosphoric acid)
But on treatment of PCl5 with heavy water (D2O) only phosphorus oxychloride if formed with
the liberation of 2 molecules of deuterium chloride as a side product. The reaction involved
is:
PCl
5 + D
2O → POCl
3 + 2DCl (phosphorus oxychloride)
................................ Advertisement ................................
36.What happens when PCl5 is heated?
Ans:
Phosphorus forms two type of halides i.e phosphorus trihalides (PCl3) and phosphorus pentahalide
PCl5. In PCl5 phosphorus undergoes sp3 d hybridization and has trigonal bipyramidal structure
.It has three equatorial P-Cl bonds and two axial P-Cl bonds which are different. The axial
bonds(219pm) are larger than equatorial bonds(204pm). PCl5 is thermally less stable than
PCl3.On heating it sublimes but decomposes on stronger heating into trichloride and chlorine.The
reaction involved is as under:
heat
PCL
5 → PCL
3 + CL
2
It is a reversible reaction,in which PCl
3 combines with Cl
2 to form PCl
5.
37.What happens when white phosphorus is heated with concentrated NaO Hsolution in an inert atmosphere of CO 2?
Ans:
Phosphorus exist in many allotropic forms. The three main forms are:
1) White Phosphorus
2) Red Phosphorus
3) Black Phosphorus
White Phosphorus is obtained from phosphorite rock with coke and sand. It consist of P4
units.The four P- atoms lie at the corners of a regular tetrahedron. It is less table and
therefore more reactive than other allotropic forms of Phosphorus. On heating with concentrated
NaOH in an inert environment of CO2 following reaction takes place:
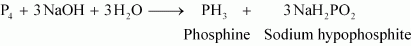
Phosphine (PH 3) is formed.This reaction is an example of disproportionation reaction in which oxidation state of phosphorus decreases from 0 in P4 to -3 in PH 3,while it increases from 0 in P 4 to +1 in NaH 2PO 2.
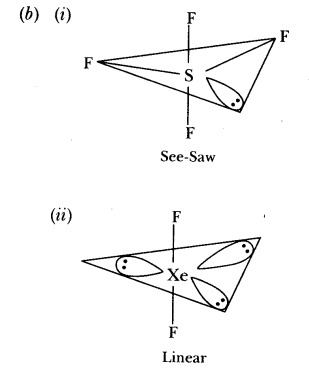
38.Write the structures of the following molecules: (i) H 2SO 3 (ii) XeOF 4
Ans:
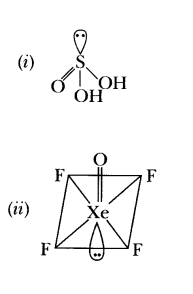
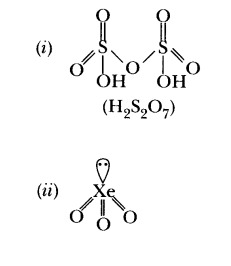
39.Write the structures of the following: (i) H 2S 20 7 (ii) Xe0 3
Ans:
40.Give reasons for the following:
(i) N
2 is less reactive at room temperature.
(ii) H
2 Te is the strongest reducing agent amongst all the hydrides of group 16-elements.
(iii) Helium is used in diving apparatus as a diluent for oxygen.
Ans:
(i) It is due to presence of triple bond which has high bond dissociation enthalpy.
(ii)H
2Te has longest bond length which has lowest bond dissociation enthalpy.
(iii) It is because helium is less soluble than N
2 in blood and does not cause pain.
................................ Advertisement ................................
41.Why does boron triflouride behave as a Lewis acid ?
Ans:
The electric configuration of boron is ns
2 np
1.It has three electrons in its valence shell. Thus, it can form only three covalent
bonds. This means that there are only six electrons around boron and its octet remains incomplete.
When one atom of boron combines with three fluorine atoms, its octet remains incomplete.
Hence, boron trifluoride remains electron-deficient and acts as a lewis acid.
42.(a) Which poisonous gas is evolved when white phosphorus is heated with Cone. NaOH solution?
Write the chemical equation.
(b) Write the formula of first noble gas compound prepared by N. Bartlett. What inspired
N. Bartlett to prepare this compound?
(c) Fluorine is a stronger oxidising agent than chlorine. Why?
(d)Write one use of chlorine gas.
(e)Complete the following equation:
CaF
2 + H
2S0
4 ———>
Ans:
a) Phosphine gas is formed.
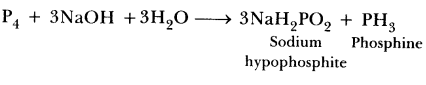
(b)Xe+PtFg. The comparable ionisation enthalpy of 02 molecule (1175 KJ mol-1) and Xe (1170 KJ mol-1) inspired Neil Bartlett to prepare this compound.
(c) It is due to low bond dissociation enthalpy, higher hydration energy of F- and high electron gain enthalpy.
(d) It is used as bleaching agent and disinfectant.
(e) CaF 2 + H 2S0 4 ———–> CaS0 4 + 2HF.
43.(a) Account for the following:
(i) Bi(V) is stronger oxidizing agent than Sb(V). (ii) H—O—I is a weaker acid than H—O—Cl.
(iii) Bond angle decreases from H
2O to H
2S. (b)Draw the structures of the following: (i) SF
4
(ii) XeF
2
................................ Advertisement ................................
(a) (i) Bi3+ is more stable than Sb3+ due to inert pair effect. Bi5+ can gain 2 electrons to form Bi3+. That is why Bi5+
is stronger oxidising agent than Sb5+.
(ii) It is because ‘Cl’ is more electronegative than ‘I’.
(iii) It is because oxygen is more electronegative and smaller in size than sulphur.
44.Name the two most important allotropes of sulphur. Which one of the two is stable at room temperature? What happens when the stable form is heated above 370 K?
Ans:
(i) Rhombic sulphur (α-sulphur)
(ii) Monoclinic sulphur (β-sulphur)
Rhombic sulphur is more stable at room temperature.When Rhombic sulphur is heated above
370 K, it changes to monoclinic sulphur.
45.(i) Write the conditions to maximize the yield of H2S04 by contact process.
(ii) Why is K
a1< < K
a2 for H
2S0
4 in water?
(i)Manufacture of sulphuric acid by Contact process involves three steps.
1. Burning of ores to form SO2
2. Conversion of SO2 to SO3 by the reaction of the former with O2 (V2O5 is used in this
process as a catalyst.)
3. Absorption of SO3 in H2SO4 to give oleum (H2S2O7)
The key step in this process is the second step. In this step, two moles of gaseous reactants
combine to give one mole of gaseous product. Also, this reaction is exothermic. Thus, in
accordance with Le Chatelier's principle, to obtain the maximum amount of SO3 gas, temperature
should be low and pressure should be high.
(ii) H
2S0
4is a strong acid, therefore, its K is very high as it dissociates into H
3O+ and HS0
4 almost completely.
The dissociation of HS0
4 to H
30+ and SO-2 is slow, therefore, is much lower than K
a1
................................ Advertisement ................................
46.Nitrogen exists as diatomic molecule and phosphorus as P4. Why?
Nitrogen owing to its small size has a tendency to form pπ−pπ multiple bonds with itself. Nitrogen thus forms a very stable diatomic molecule, N2. On moving down a group, the tendency to form pπ−pπ bonds decreases (because of the large size of heavier elements). Therefore, phosphorus (like other heavier metals) exists in the P4 state.
47. Which aerosols deplete ozone?
Freons and chlorofluorocarbons(CFCs) are aerosols that accelerate the depletion of ozone.In the presence of ultraviolet radiations,molecules of CFCs break down to form chlorine free radicals that combine with ozone to form oxygen.
48.How is SO 2 an air pollutant?
Ans:
Following points proves that SO2 is a air pollutant. a)Sulphur dioxide when combined with
the water vapour present in the atmosphere forms sulphuric acid.This results in acid rain.Acid
rain is harmful for plants, soil and buildings, specially those made of marbles.
b)Even in very low concentrations, SO
2 causes irritation in the respiratory tract.It causes eye and throat irritation and
also damages the larynx resulting in breathlessness.
c)It is very harmful for plants.Normally if the plants are exposed too much to SO
2, it leads to discoloration of leaves, which is called as chlorosis.This happens because
of the formation of chlorophyll is affected by the presence of sulphur dioxide.
49.List the uses of Neon and argon gases.
Ans:
Uses of neon gas:
(i) It is mixed with helium to protect electrical equipments from high voltage.
(ii) It is filled in discharge tubes with characteristic colours.
(iii) It is used in beacon lights.
Uses of Argon gas:
(i) Argon along with nitrogen is used in gas-filled electric lamps. This is because Ar is
more inert than N.
(ii) It is usually used to provide an inert temperature in a high metallurgical process.
(iii) It is also used in laboratories to handle air-sensitive substances.