List of Questions and Answers
Q 1. As per psychology what is individual differences?
Ans: It refers to the distinctiveness and variations in people’s characteristics and behaviour patterns.
Q 2. When the behaviour is influenced more by situational factors it is called as __________.
Ans: Situationism
Q 3. What is Assessment as per Psychology?
Ans: It refers to the measurement of psychological attributes of individuals and their evaluation, wherein multiple ways are involved in comparing the attributes.
Q 4. What are the important assessment attributes for Psychologist?
Ans:
Intelligence : It is the global capacity to understand the world, think in a sensible
and logical manner, and use the resources available with you effectively to face challenges.
Aptitude: refers to an individual's underlying potential to acquire any new skills.
Interest: refers to an individual’s choice for engaging in one or more specific activities
in comparison to others.
Personality: refers to an individual’s strong characteristics that make this person different
from others. Personality assessment helps us to explain an individual’s behaviour and predict
how she/he will behave in future.Whether the individual will be dominant or submissive, moody
or emotionally stable, introvert or extrovert etc.
Values: refers to an individual’s strong and lasting beliefs about an ideal mode of behaviour.
Assessment of values helps in understanding the dominant values of a person (example : political,
religious, social or economic).
................................ Advertisement ................................
Q 5. What are the Assessment Methods used by Psychologist?
Ans:
Psychological Test: is used to measure an individual's mental and/or behavioural characteristics.The
tests are done on psychological attributes like intelligence, aptitude, values, personality.These
tests are used for the purpose of clinical diagnosis, guidance, personnel selection, placement
and training.
Interview: is a process of getting information from a person on a one-to-one basis.It
is used mainly by employer to select employees for his organisation, used by salesperson
by making door-to-door visit to sell the product, counsellor interacts with a client,journalist
interviewing important people.
Case Study: in-depth study of an individual's psychological attributes , its history
regarding his/her psychosocial and physical environment.Case studies are widely used by clinical
psychologists.Case studies on the lives of great people can also be highly inspiring for
those willing to learn from their life experiences. Case study involves gathering of data
based on different methods like interview, observation, questionnaires,psychological tests
etc.
Observation: is a systematic organised and objective procedure to record behavioural
phenomena that occurs naturally in real time.For example mother-child interactions.
Self-Report: Self-Report is a method in which a person provides factual information about
herself/himself and/or opinions, beliefs, etc. that s/he holds. Such information may be obtained
by using an interview schedule or a questionnaire, a psychological test, or a personal diary.
Q 6. How do psychologists characterise and define intelligence.
Ans:
For Psychologists intelligence is the key parameter that shows how individuals differ from
one another. The attributes noticed in an intelligent person are mental alertness, ready
wit, quickness in learning, and ability to understand relationships.
As per oxford dictionary, intelligence is defined as the power of perceiving, learning,
understanding, and knowing.
As per Alfred Binet the first psychologists who worked on intelligence , defines intelligence
as the ability to judge well, understand well, and reason well.
Wechsler psychologists defined intelligence as the global and aggregate capacity of an individual
to think rationally, act purposefully, and deal effectively with her/his environment.
Gardner and Sternberg psychologists says that an intelligent individual not only adapts
to the environment, but also actively modifies or shapes it.
................................ Advertisement ................................
Q 7. Explain briefly the multiple intelligences identified by Gardner?
Ans:
As per Gardner , intelligence is not a single entity; rather distinct types of intelligences
exist
Here are some important points as what Gardner feels on multiple intelligence.
a) intelligences are independent of each other.
b) Different types of intelligence interact and work together to find a solution to a problem.
Mr Gardner Identified 8 types of intelligence and here are the details:
Linguistic skill involved in using the language, how well he/she reads, speaks, writes
and understand others.Poet and Writers are very strong in linguistic intelligence.
Logical-Mathematical skill mainly possess problem solving ability, very high on thinking
logically,good at abstract reasoning and can solve mathematical problems with ease.Scientists
and Nobel prize winners are good example with Logical-Mathematical Intelligence.
Spatial skill is more of understanding visual images and patterns. It refers to the abilities
involved in forming, using, and transforming mental images.Pilots, sailors, sculptors, painters,
architects, interior decorators, and surgeons are likely to have highly developed spatial
intelligence.
Musical skill has more detail understanding of producing, creating and manipulating musical
patterns. Persons high on this intelligence are very sensitive to sounds and vibrations,
and in creating new patterns of sounds.
Bodily-Kinaesthetic is to make use of your whole body for problem solving or construction
of products.Athletes, dancers, actors, sportspersons, gymnasts, and surgeons are likely to
have such kind of intelligence
Interpersonal skill involves understanding behaviours , their motives , feelings and
form a comfortable relationship with others.Psychologists, counsellors, politicians, social
workers, and religious leaders are likely to possess high interpersonal intelligence
Intrapersonal skill deals with knowing one's internal strengths and limitations and using
that knowledge to effectively relate to others.Philosophers and spiritual leaders present
examples of this type of intelligence.
Naturalistics skill involves awareness of our relationship with natural world, i.e. analysing
the beauty of species present, flora and fauna etc. Hunters, farmers, tourists, botanists,
zoologists, and bird watchers possess more of naturalistic intelligence.
................................ Advertisement ................................
Q 8. Triarchic theory of intelligence was proposed by _________.
Ans:
Robert Sternberg
Q 9. How does the triarchic theory help us to understand intelligence?
Ans:
Triarchic theory of intelligence was proposed by Robert Sternberg in the year 1985. As per
Sternberg intelligence is defined as "the ability to adapt,to shape and select environment
to accomplish one’s goals and those of one’s society and culture".
According to the theory, there are three basic types of intelligence and they are : Componential,
Experiential, and Contextual.
Componential also called as analytical intelligence mainly deals with the analysis of
information to solve a particular problem.
There are three components involved with Componential intelligence:
Knowledge acquisition component : this component is responsible to learn and acquire
knowledge to carry out the task.
meta or a higher order component : this component deal with plans about how to do the
task.
performance component : this component involves of actually getting the task done.
Experiential also called as creative intelligence deals in past experiences to solve
problems.Persons high on this aspect integrate different experiences in an original way to
make new discoveries and inventions.
Contextual also called as practical intelligence deals with environmental demands encountered
on a daily basis.Persons high on this aspect easily adapt to their present environment or
select a more favourable environment than the existing one, or modify the environment to
fit their needs. Therefore, they turn out to be successful in life.
................................ Advertisement ................................
Q 10. "Any intellectual activity involves the independent functioning of three neurological systems". Explain with reference to PASS model.
PASS Model was developed by J.P.Das , Jack Naglieri and Kirby in the year 1994. As per them three neurological systems called the functional units of brain are responsible for
- Arousal / Attention
- Simultaneous and Successive Processing
- Planning
- It helps person to process any information
- Arousal makes you focus your attention on your task which needs to be completed.
Simultaneous and Successive Processing
- Simultaneous and Successive Processing deals with how the brain processes the information, builds the relation between the data available and integrate them into a meaningful pattern which is understandable.
- Simultaneous processing helps you in grasping the meaning and relationship between the given abstract figures.
- Successive processing takes place when you have all the required information serially and how one step will lead to the next step and so on.
Planning
- Planning is an important feature of intelligence.
- It comes into picture once the information is collected and processed.
- It allows us to think of the possible courses of action, implement them to reach a target, and evaluate their effectiveness.
- If a plan fails, it is modified to suit the requirements of the task being done.
Q 11. What is Intelligence Quotient (IQ)?How do psychologists classify people on the basis of their IQ scores?
IQ refers to mental age divided by chronological age, and multiplied by 100.
IQ = MA/CA x 100
- William Stern, a German psychologist, devised the concept of Intelligence Quotient.
- When MA = CA , IA = 100
- If MA > CA, IQ > 100
- If MA < CA, IQ < 10
- People with an IQ scores in the range of 90–110 have normal intelligence.
- People with an IQ below 70 are suspected to have "mental retardation".
- People with an IQ above 130 are considered to have exceptional talents.
| IQ Range | Descriptive Label | Percent in the Population |
|---|---|---|
| Above 130 | Very superior | 2.2 |
| 120-130 | Superior | 6.7 |
| 110-119 | High Average | 16.1 |
| 90-109 | Average | 50.0 |
| 80-89 | Low Average | 16.1 |
| 70-79 | Borderline | 6.7 |
| Below 70 | Mentally challenged/retarded | 2.2 |
................................ Advertisement ................................
Q 12. Find out the IQ of a 14-year-old child with a mental age of 16.
IQ = 16/14 x 100 = 114
Q 13.___________was defined by Binet and Simon as being two mental age years below the chronological age.
Retardation
Q 14.State few characteristics of emotionally intelligent persons.
The characteristics of emotionally intelligent persons are :
- Perceive and be sensitive to your own’s feelings and emotions.
- Perceive and be sensitive to others people’s emotions by paying attention to their tone, body language and facial expressions.
- Relate your emotions to your thoughts so that you take them into account while solving problems or making decisions.
- Understand the powerful influence of the nature and intensity of your emotions.
- Control your emotions and their expression while dealing with self and others to promote harmony and peace.
Q 15.Analyse the features of creativity tests.
Here are the features of creativity tests:
- One of the important feature is creativity test are they are open ended,which means that it makes a person think different answers to the questions or problems based on their experiences which comes their way.
- Creativity test involves off-the-beaten track divergent thinking and has the ability to produce different ideas.
- The tests require people to think creatively for example ability to think of a variety of ideas on a given topic/situation, alternative ways of looking at things, problems or situations etc.
- Creativity test makes a person to see new relationships between seemingly unrelated things, ability to guess causes and consequences, ability to put things in a new context, etc.
................................ Advertisement ................................
Q 16.Bring out three points of difference between Individual and Group tests
| Individual Test | Group Test |
|---|---|
| An individual test is the one that can be given to one person at a time. | A group test can be given to several persons simultaneously. |
| Individual tests require the test administrator to establish a rapport with the subject and be sensitive to her/his feelings, moods and expressions during the testing session. | Group tests, however, do not allow an opportunity to be familiar with the subjects’ feelings |
| Individual tests allow people to answer orally or in a written form or manipulate objects as per the tester’s instructions. | Group tests generally seek written answers usually in a multiple-choice format. |
Q 17.Draw the normal curve and show the percentagewise distribution of IQ scores in general population.
Normal :
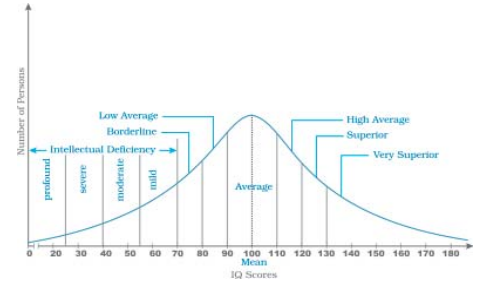
Percentage wise distribution of IQ scores in general population
| IQ Range | Descriptive Label | Percent in the Population |
|---|---|---|
| Above 130 | Very superior | 2.2 |
| 120-130 | Superior | 6.7 |
| 110-119 | High Average | 16.1 |
| 90-109 | Average | 50.0 |
| 80-89 | Low Average | 16.1 |
| 70-79 | Borderline | 6.7 |
| Below 70 | Mentally challenged/retarded | 2.2 |
................................ Advertisement ................................
Q 18.Explain the following psychological attributes :
(i) Intelligence
(ii) Aptitude
(i) Intelligence : is the global capacity to understand the world, think rationally, and use the available resources effectively when faced with challenges. Intelligence tests provides a global measure of a person’s general cognitive competence, including the ability to profit from schooling.
In general, students having low intelligence are not likely to do so well in school-related examinations, but their success in life is not associated only with their intelligence in exams test scores.
(ii) Aptitude : refers to an individual’s underlying potential for acquiring skills. Aptitude tests are used to predict what an individual will be able to do if given proper environment and training. A person with high mechanical aptitude can profit from appropriate training and can do well as an engineer.
Same way a person having high language aptitude can be trained to be a good writer.
Q 19.Defined Mental Retardation.Analyse the levels of Mental Retardation.
Mental retardation is defined as "significantly sub-average general intellectual functioning existing concurrently with deficits in adaptive behaviour and manifested during the developmental period".
The different levels of retardation are:
- mild retardation (IQs 55–69),
- moderate retardation (IQs 40–54),
- severe retardation (IQs 25–39), and
- profound retardation (IQs below 25)
The people with moderate retardation lag behind their peers in language and motor skills. They need to be trained in self-care skills, and simple social and communication skills.They need little bit of supervision in everyday tasks.
Individuals with profound and severe retardation are incapable of managing life and need constant care for their entire lives.
................................ Advertisement ................................
Q 20.What is Cognitive Assessment System(CAS)?
It is a mixture of verbal and non verbal tasks which is used to measure cognitive functions in individual falling in age group of 5-18 yrs. The result of the assessment can be used as a remedy in cognitive deficit children with learning problems.
Q 21.Analyse the role of hereditary influences on intelligence.
To know about the hereditary influences on intelligence, the analysis is conducted mainly on twins and adopted children.
The observation are as follows:
- The intelligence of identical twins brought up together mostly shows 90% similarity.
- Twins separated in their childhood also shows similarity in terms of behaviour, personality and intellectual characteristics.
- The intelligence of identical twins brought up in different environments is almost 72%.
- Fraternal twins brought up together shows intelligence similarity of about 60%.
- Brothers and sisters brought up together shows intelligence similarity of about 50%.
- Siblings which are brought up separately shows intelligence similarity of about 25%.
- In case of adopted children intelligence is more close towards their biological parents rather than adoptive parents.As they grow , they slowly start picking up and get closer with intelligence of their adoptive parents.
- Children which are comes from deprived homes and later adopted in families having ,good food , good family background and quality schooling makes their intelligence improved.
- So mostly all Psychologists come to a conclusion that intelligence is a product of complex interaction of heredity (nature) and environment (nurture).
Q 22.What is contextual intelligence?
Ans: Contextual also called as practical intelligence is the ability to deal with environmental demands that we come across on a daily basis.
Q 23.Define Aptitude.
Ans: It is a combination of characteristics that indicates an individual’s capacity to acquire some specific knowledge or skill after training.
................................ Advertisement ................................
Q 24.Distinguish between simultaneous processing and successive processing with examples.
Ans:
| Simultaneous Processing | Successive Processing |
|---|---|
| When you know how to relate among the various concepts and get them all together to form something meaningful it is called as simultaneous processing. | Successive processing is when you know all the steps and required information serially so that one leads to the recall of another. |
| For example, consider Raven’s Progressive Matrices (RPM) Test, in which the model is given and from that a part has been removed that needs to be fixed. You are suppose to choose one of the six options that best completes the design. | For example learning of digits, alphabets, multiplication tables, etc. successive processing |
Q 25.Are there cultural differences in the conceptualisation of intelligence?
Ans:
Culture plays a very important role in shaping the intelligence.
Vygotsky, a Russian psychologist believes that culture provides a social context in which
people live, grow, and understand the world around them.
As per Sternberg’s he believes that intelligence is a product of culture
Intelligence does have an impact on cultural parameters like customs, beliefs, attitudes,
and achievements in art and literature.
There are two main intelligence concepts that comes into the picture when we discuss about
culture and they are: technological intelligence and integral intelligence
Technological Intelligence
- Mostly observed in technologically advanced societies.
- These societies has a person well versed in skills like attention,observation,analysis, speed, performance, and achievement.
- Technological intelligence is not popular in Asian and African societies.
- Mostly adopted by Indian culture which deals with connection with social and world environment.
- The sanskrit word “buddhi” which means intelligence is the knowledge of one’s own self based on conscience, will and desire.
- As per Indian Tradition following aspects plays a very important role:
- Cognitive capacity deals with sensitivity to context, understanding, discrimination, problem solving, and effective communication.
- Social competence deals with respect for social order, commitment to elders, the young and the needy, concern about others, recognising others perspectives.
- Emotional competence deals with self-regulation and self-monitoring of emotions, honesty, politeness, good conduct, and self-evaluation.
- Entrepreneurial competence deals with commitment, persistence, patience,hard work, vigilance, and goal-directed behaviours.
................................ Advertisement ................................
Q 26.How can you differentiate between verbal and performance tests of intelligence?
Ans:
| Verbal Test | Performance Test |
|---|---|
| Verbal test includes response either orally or in written form. | Performance test includes a task wherein the individual requires to manipulate or change the material to get this task done. |
| This test is conducted on literate people as it needs the individual to write or talk. | Can be conducted on individuals from different cultures and does not include any writing process |
Q 27.All persons do not have the same intellectual capacity. How do individuals vary in their intellectual ability? Explain.
Ans:
Every individual differ in their physical appearances , and at the same they do differ in
their intellectual capacity.
An individual intellectual abilities is divided into two parts Intellectual Deficiency and
Intellectual Giftedness.
Intellectual Deficiency: children who have difficulty in learning a very simple task
are said to have low intellectual and they are mostly termed as mentally challenged or mentally
retarded.
To be categorized as mentally retarded there three features which needs to be noted:
- The IQ has to be below 70 and they are judged as having sub-average intelligence.
- The second relates to deficits in adaptive behaviour i.e the inability to be independent and deal with everyday’s task.
- The individuals in this category has to be observed right from childhood till the age of 18.
The different levels of retardation are:
- mild retardation (IQs 55–69) : Mild retardation people are little slower in comparison to other their peers, but they can do their jobs and handle families independently.
- moderate retardation (IQs 40–54) :The people with moderate retardation lag behind their peers in language and motor skills. They can be trained for social, communication skills and self care skills.
- severe retardation (IQs 25–39) : are incapable of managing life and need constant care for their entire lives.
- profound retardation (IQs below 25) : are incapable of managing life and need constant care for their entire lives.
Individual following in this category show high performance , very successful because of their outstanding personalities. Their IQ will always be 130 and above. Children with gifted intellectual show larger attention span, good recognition memory, preference for novelty, sensitivity to environmental changes, and early appearance of language skills.
................................ Advertisement ................................
Q 28.What are the characteristics of gifted children?
Ans:
Some important characteristics of gifted children are :
- Advanced logical thinking, questioning and problem solving behaviour.
- High speed in processing information.
- Superior generalisation and discrimination ability.
- Advanced level of original and creative thinking.
- High level of intrinsic motivation and self-esteem.
- Independent and non-conformist thinking. • Preference for solitary academic activities for long periods.
Q 29.________ behaviour refers to a person’s capacity to be independent and deal effectively with one’s environment.
Ans:Adaptive
Q 30. ___________ is exceptional general ability shown in superior performance in a wide variety of areas.
Ans: Giftedness
Q 31.Which of the two, IQ or EQ, do you think would be more related to success in life and why?
Ans:
EQ is mean to express to Emotional intelligence and
IQ is meant to express intelligence.
EQ makes a person successful and as per research done by psychologist with EQ it benefits
:
- To deal with students who are affected by stresses and challenges of the outside world.
- Success in academic achievement.
- Encourage cooperative behaviour and reduce their antisocial activities.
- Prepares students to face the challenges of life outside the classroom.
................................ Advertisement ................................
Q 32.How is "aptitude" different from "interest" and "intelligence"? How is aptitude measured?
Ans:
Following points will help understand how aptitude, is different from interest and intelligence.
- Aptitude refers to special abilities in a particular field of activity. It is a combination of characteristics that indicates an individual’s capacity to acquire some specific knowledge or skill after training.
- The knowledge of aptitude can help us to predict an individual’s future performance.
- Interest is a preference for a particular activity whereas aptitude is the potentiality to perform that activity.
- A person may be interested in a particular job or activity, but may not have the aptitude i.e the skills required to take the interest further. Similarly, a person may have the potentiality for performing a job, but may not be interested in doing that. In both cases, the outcome will not be satisfactory.
- Intelligence : It is the global capacity to understand the world, think in a sensible and logical manner, and use the resources available with you effectively to face challenges.
- An intelligent person are mental alertness, ready wit, quickness in learning, and ability to understand relationships.
- Intelligence is also defined as the power of perceiving, learning, understanding, and knowing.
- Clerical Aptitude, Mechanical Aptitude, Numerical Aptitude, and Typing Aptitude are independent aptitude tests.
- Multiple Aptitude Tests exist in the form of test batteries, which measures aptitude in several separate but homogeneous areas.
- Differential Aptitude Tests (DAT), the General Aptitude Tests Battery (GATB), and the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) are well-known aptitude test batteries.
- DAT is most commonly used in educational settings. It consists of 8 independent subtests: (i) Verbal Reasoning, (ii) Numerical Reasoning, (iii) Abstract Reasoning, (iv) Clerical Speed and Accuracy, (v) Mechanical Reasoning,vi) Space Relations, (vii) Spelling, and (viii) Language Usage.
Q 33.What is Assessment ?
Ans: Assessment refers to the measurement of psychological attributes of individuals and their evaluation, often using multiple methods in terms of certain standards of comparison.
Q 34.Explain theory of Primary Mental Abilities by Louis Thurstone ?
Ans:
As per Louis Thurstone intelligence consists of seven primary abilities, each of which is relatively independent of the others.
These primary abilities are:
- (i) Verbal Comprehension (grasping meaning of words, concepts, and ideas),
- (ii) Numerical Abilities (speed and accuracy in numerical and computational skills),
- (iii) Spatial Relations (visualising patterns and forms),
- (iv) Perceptual Speed (speed in perceiving details),
- (v) Word Fluency (using words fluently and flexibly),
- (vi) Memory (accuracy in recalling information), and
- (vii) Inductive Reasoning (deriving general rules from presented facts).